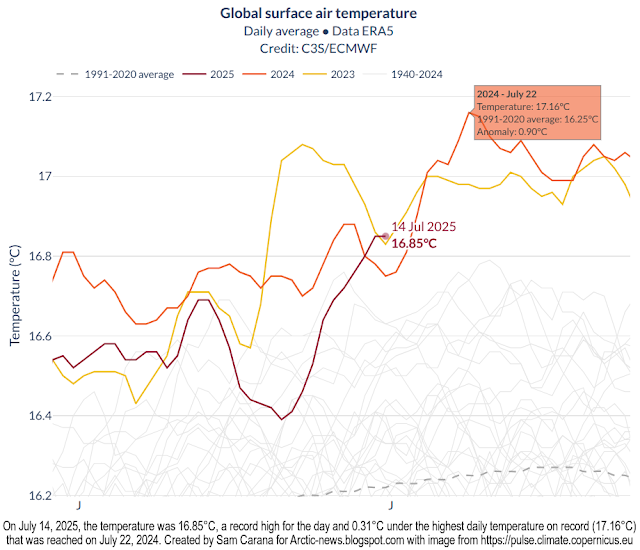
Forests come with many climate benefits. Trees take carbon out of the atmosphere and store the carbon in the trees and in the soil, thus reducing global warming. Less carbon dioxide in the atmosphere also reduces ocean acidification. The top layer (canopy) of rainforests contains giant trees that can grow to heights of 75 m (about 250 ft) or more. The canopy prevents much sunlight from reaching the ground, thus cooling the surface locally. Trees hold the soil together and can pump up water from deep in the soil and, through evaporation, keep the surface and soil cool, thus also avoiding erosion and reducing fire hazards.
So, trees are responsible for cooling in many ways. Trees can darken the surface, which can cause more sunlight to be absorbed, thus resulting in more warming, but trees can also cause cooling in another way. Trees also release terpines and other biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) into the air. These BVOCs can react chemically in the atmosphere to form aerosols that reflect incoming solar radiation and thereby cause global cooling. These aerosols can also act to start clouds to form that result in rainfall and that shade the surface, reflecting more solar radiation back into space and thus cause further global cooling.
While BVOCs have many benefits, they can also indirectly increase potent greenhouse gases including ozone and methane by depleting hydroxyl. A study led by Gillian Thornhill found that this could cause half the cooling effects of BVOCs to be lost. A recent study led by James Weber found that, when all the effects are combined, they can reduce the net climate benefit of wide scale tree-planting by up to one third.
The above image shows that organic matter aerosol optical thickness (55 nm) as high as 0.93 τ was recorded over North Australia on October 14, 2025 06:00 UTC.
A recent study led by Hannah Carle finds that a transition from sink to source has occurred for the aboveground woody biomass of the Australian moist tropical forests. Forests need to be supported and not just for their capacity to sequester carbon. The net climate benefit of trees is huge and is underestimated. While trees can cause some warming, they also cause more cooling. Their BVOCs are responsible for some depletion of hydroxyl, but this should be no reason to withhold support for forests. Instead, climate action should strongly support forests, while greater hydroxyl abundance is best accomplished by cleaning up industry sectors such as agriculture, transport and electricity generation.
IPCC downplays the temperature rise
The IPCC downplays the temperature rise in efforts to hide some of the most effective and necessary action, e.g. by presenting the impact of land use, gases and aerosols in most peculiar ways. Instead of comparing the climate impact of forests versus agriculture in commonly comprehensible language, such as a rise in degrees Celsius, the IPCC uses technical terms to make things less comprehensible for the typical reader (and voter).
As an example, the IPCC seeks to present deforestation as a change in land use that results in greater cooling, e.g. by arguing that deserts reflect more light back into space. As another example, the IPCC makes it look as if the temperature started rising only from 1850-1900, in efforts to hide the huge impact of deforestation that took place before those years.
People have been herding animals and burning or cutting down trees for thousands of years. Before the Industrial Revolution, wood and plants were used for shelter and as building material. Plants also provided food for people and fodder for animals that were herded and that were used for food, ploughing, hunting, herding and transport. Biomass was also burned for heating, preparing food, cooking water, lighting and protection.
Deforestation was the result of people's growing demand for biomass. Deforestation also increased due to trees getting cut down or burned as demand grew for land that could be used for urban purposes, as pasture or to grow more food and fodder.
Deforestation was the result of people's growing demand for biomass. Deforestation also increased due to trees getting cut down or burned as demand grew for land that could be used for urban purposes, as pasture or to grow more food and fodder.
 |
| [ click on images to enlarge ] |
The 1850-1900 period that the IPCC uses as base to measure the temperature rise doesn't reflect pre-industrial well, for a number of reasons. Firstly, people's emissions pushed up temperatures long before that. Secondly, the 1850-1900 period was dominated by burning coal to provide heating and energy, which came with sulphur co-emission causing surface cooling, masking the temperature rise.
The rise from 1750 to 2024 in methane, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide is illustrated by the image on the right, based on IPCC and WMO data.
While emission by people did accelerate since the start of the Industrial Revolution and even more recently, the rise in emission by people had already started thousands of years ago with growth in agriculture, herding of animals and associated deforestation, as illustrated by the combination image below, based on Ruddiman et al. (2015).
 |
| [ from earlier post ] |
The temperature has risen accordingly since those times. Deforestation and growth in irrigation and numbers of people, livestock and herded animals and their crop waste, sewage and manure resulted in emissions. While much of the forests could initially regrow, the net result was a gradual loss of trees and the cooling aerosols they previously provided and a gradual growth in emissions such as methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and black carbon (soot).
A 2013 study by Bond et al. calculates that black carbon has a warming effect of about 1.1 W/m², part of which is caused by black carbon darkening the snow and ice cover since pre-industrial times, as discussed on the aerosols page. By some calculations, the temperature in 1520 had risen by 0.29°C, compared to thousands of years earlier.
A 2013 study by Bond et al. calculates that black carbon has a warming effect of about 1.1 W/m², part of which is caused by black carbon darkening the snow and ice cover since pre-industrial times, as discussed on the aerosols page. By some calculations, the temperature in 1520 had risen by 0.29°C, compared to thousands of years earlier.
September 2025 temperature anomaly
The image below shows how much higher the September 2025 temperature was than it was in 1951-1980.
The above image shows that the September 2025 temperature anomaly was high over both poles and especially high over some areas in Antarctica, where anomalies higher than +10°C versus 1951-1980 were recorded.
As the image below shows, the temperatures recorded over Antarctica throughout September 2025 were higher than in most earlier years, while a record daily high temperature was recorded on October 10, 2025, a +3.62°C anomaly compared to 1979-2000. The inset shows high temperature anomalies versus 1991-2020 at both poles on October 10, 2025.
The image below shows that the global September 2025 temperature anomaly was 1.306°C higher than 1951-1980. Note that the 2025 anomalies were reached under borderline La Niña conditions that suppress temperatures and that the monthly temperature anomaly would be significantly higher when calculated from 1850-1900, which is typically used by the IPCC as baseline.
 |
| [ Temperature Rise, click on images to enlarge ] |
The full historic temperature rise and the rise to come soon could be much higher, as described on the image and below. The inset is also displayed and discussed in more detail below.
Emissions and Temperature Rise
The observed temperature rise (O) is actually masked by aerosols (M) and the IPCC only includes the rise from the period 1850-1900, ignoring the rise before the period 1850-1900 (P) and the rise that took place to negate the natural fall in temperature. Aerosols could fall out of the air soon, so when adding things up (E1+E2), the historic temperature rise from pre-industrial (O+M+P) is huge.
When also taking into account that the temperature would have fallen naturally, i.e. in the absence of these emissions and in line with Milankovitch cycles (E3), the rise caused by people to negate that could also be included (H), adding up to an even higher historic temperature rise (O+M+P+H).
Additionally, the full impact of all past emissions may not be fully felt yet, e.g. the full effect of carbon dioxide emissions reaches its peak only a decade after emission (E4). Furthermore, humans are likely to continue to cause emissions in the near future (E5). Finally, additional releases of greenhouse gases are likely to come from what was once called permafrost and from sinks turning into sources, resulting in an additional rise that's already baked into the cake (E6). Therefore, the historic rise plus the rise to come soon (O+M+P+H+F) may approach 5°C.
The diagram below further illustrates the importance of feedbacks and deforestation. Removal of trees has caused deforestation and soil carbon loss since prehistoric times, in turn causing emissions including carbon dioxide, methane and black carbon, while also reducing cooling aerosols released by trees and while also reducing the heat buffer of evaporation that previously cooled the atmosphere. Since prehistoric times, burning wood and deforestation has caused emissions of black carbon and dust that blackened the snow and ice cover, thus speeding up its decline.
 |
| [ from earlier post ] |
 |
| [ from earlier post ] |
Climate Emergency Declaration
UN secretary-general António Guterres recently spoke about the need for “a credible global response plan to get us on track” regarding the international goal of limiting the global temperature rise. “The science demands action, the law commands it,” Guterres said, in reference to a recent international court of justice ruling. “The economics compel it and people are calling for it.”
What could be added is that the situation is dire and unacceptably dangerous, and the precautionary principle necessitates rapid, comprehensive and effective action to reduce the damage and to improve the outlook, where needed in combination with a Climate Emergency Declaration, as described in posts such as this 2022 post and this one and as discussed in the Climate Plan group.
Links
• NASA - Earth by Biome
• Nullschool.net
https://thebulletin.org/2024/05/missing-the-forest-for-the-trees-the-role-of-forests-in-earths-climate-goes-far-beyond-carbon-storage
• Aerosols
• Aboveground biomass in Australian tropical forests now a net carbon source - by Hannah Carle et al.
discussed on Facebook at:
• Pre-industrial
• The World lost one third of forests
https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/8/1/133
https://wmo.int/news/media-centre/carbon-dioxide-levels-increase-record-amount-new-highs-2024
WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin - No. 21 (issued October 15, 2025)
https://wmo.int/files/greenhouse-gas-bulletin-no-21
discussed on Facebook at:
https://www.facebook.com/groups/arcticnews/permalink/10163357891699679
• Record low Arctic sea ice volume minimum highlights methane danger
• Transforming Society
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Climate Emergency Declaration
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climate-emergency-declaration.html