by Andrew Glikson
As terrestrial adversaries keep pushing the Earth and its inhabitants to within seconds of a nuclear catastrophe, looming through heat waves, extreme fires and flood events is the huge calamity of irreversible global warming.
 |
| [ from earlier post ] |
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) reached levels well above 420 parts per million (ppm) at Mauna Lao, Hawaii, on February 13 and 14, 2022, as illustrated by the image, from an earlier post.
The image below, adapted from NOAA, shows CO₂ and other greenhouse gases such as methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) rising from 280 ppm CO₂e in 1700 to 504 ppm CO₂e in 2021. This figure of 504 ppm CO₂e could be much higher when applying a short horizon to calculate methane's Global Warming Potential.
CO₂ levels have been rising from ~315 ppm in 1950 to ~419 ppm in 2022, at an average growth rate of some 1.44 ppm/year accelerating to about 2.5 ppm/year recently.
The rate of this CO₂ rise is unprecedented in the Cenozoic (since 65 Ma) record, with perhaps the closest parallel being the aftermath of the K-T dinosaur mass extinction event, when the temperature rose by as much as ~7.5°C. According to Beerling et al. (2002) CO₂ level rose from 350–500 ppm to at least 2,300 ppm within 10,000 years following the K-T impact, at an average rate of ~0.2 ppm/year, significantly less than today's rate.
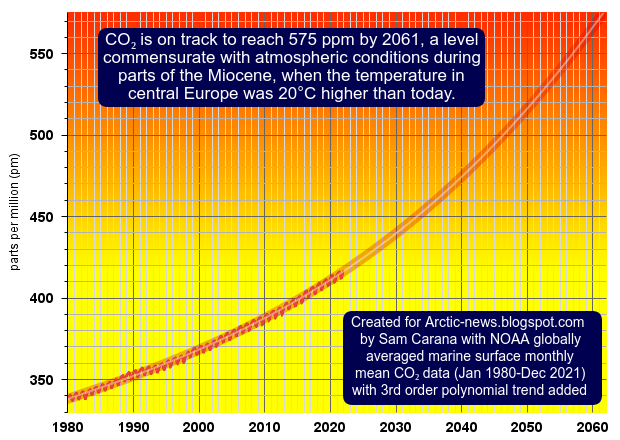
Above image shows CO₂ on track to reach 575 ppm by 2061, a level commensurate with atmospheric conditions during parts of the Miocene, when the temperature in central Europe was 20°C higher than today, as also illustrated by the image below, adapted from a 2020 study by Methner et al.
The image below further illustrates that to find CO₂ levels as high as 575 ppm, we have to go back in time millions of year, into the Miocene.
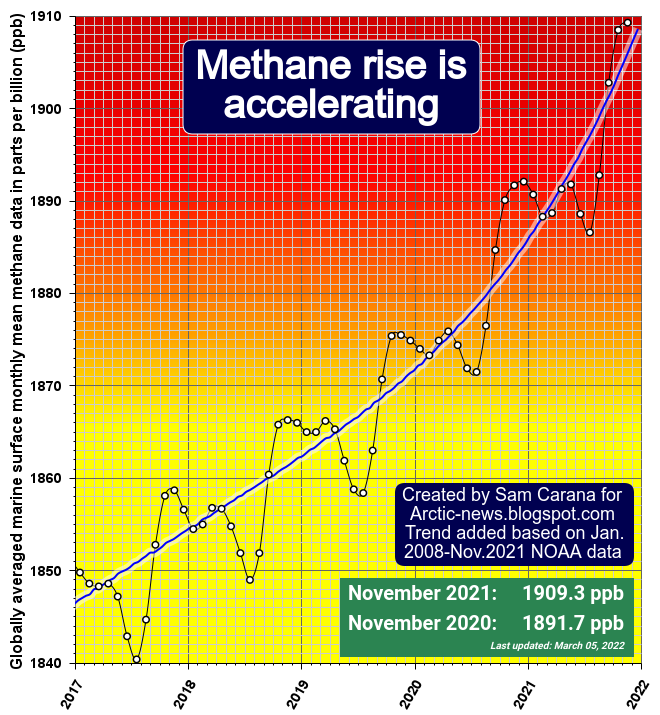
What makes current conditions even more dire is that it's not just carbon dioxide that is rising at a speed unprecedented in history, methane is rising at an even faster pace, as illustrated by the image below, from an earlier post.
Can the current climate trend be arrested, or even reversed?
The current global greenhouse gas trend is leading to one of the largest mass extinctions of species in the geological record, one of the victims being human civilization. The current focus on emission reduction overlooks a major factor, namely the amplifying feedbacks from land and oceans (Steffen et al., 2018). There is a desperate need, in addition to emission reduction, for urgent large-scale sequestration of atmospheric greenhouse gases, and for further action to combat the temperature rise.
The role of amplifying GHG feedbacks from land and oceans, leading to enhanced heating, appears to be neglected in climate negotiations. Amplifying feedbacks include:
- an increase in evaporation, raising atmospheric water vapor levels, which enhances the greenhouse gas effect;
- a decline in the polar albedo (reflection) due to large-scale lateral and vertical melting of ice;
- release of methane from degrading permafrost and from polar sediments;
- reduced CO₂ intake by warming oceans. Currently the oceans absorb between 35-42% of all CO₂ and around 90% of the excess heat;
- warming, desiccation, deforestation and fires over land areas.
 |
| Andrew Glikson |
Earth and Paleo-climate scientist
School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences
The University of New South Wales,
Kensington NSW 2052 Australia
The Asteroid Impact Connection of Planetary Evolution
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9789400763272
The Archaean: Geological and Geochemical Windows into the Early Earth
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319079073
Climate, Fire and Human Evolution: The Deep Time Dimensions of the Anthropocene
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319225111
The Plutocene: Blueprints for a Post-Anthropocene Greenhouse Earth
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319572369
Evolution of the Atmosphere, Fire and the Anthropocene Climate Event Horizon
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9789400773318
From Stars to Brains: Milestones in the Planetary Evolution of Life and Intelligence
https://www.springer.com/us/book/9783030106027
Asteroids Impacts, Crustal Evolution and Related Mineral Systems with Special Reference to Australia
https://www.springer.com/us/book/9783319745442
The Event Horizon: Homo Prometheus and the Climate Catastrophe
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783030547332
The Fatal Species: From Warlike Primates to Planetary Mass Extinction
https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783030754679