|
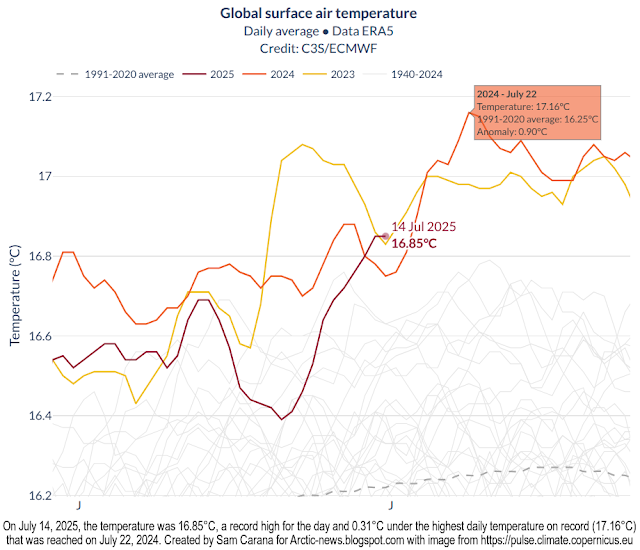
| [ June 2025 temperature anomaly, click on images to enlarge ] |
 |
| [ from earlier post, click to enlarge ] |
 |
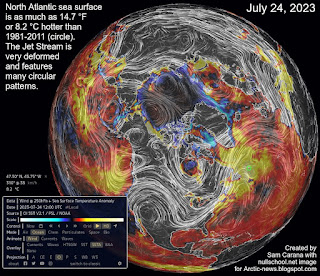
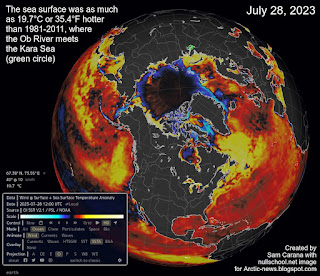
| [ marine heatwave in North Pacific ] |
 |
| [ image from: 10°C or 18°F warmer by 2021? ] |
 |
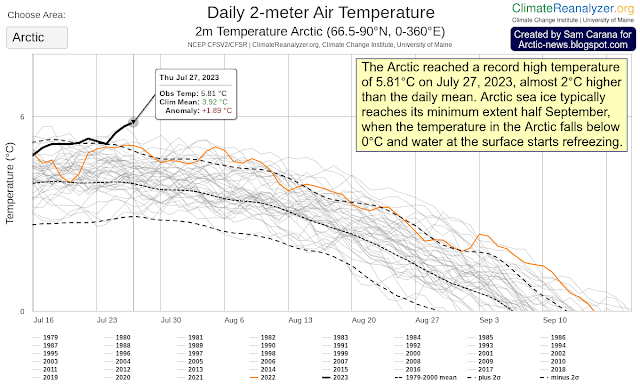
| [ Temperature rise vs 1901-2000 (ClimateReanalyzer) and vs 1850-1900 (IPCC, inset left) ] |
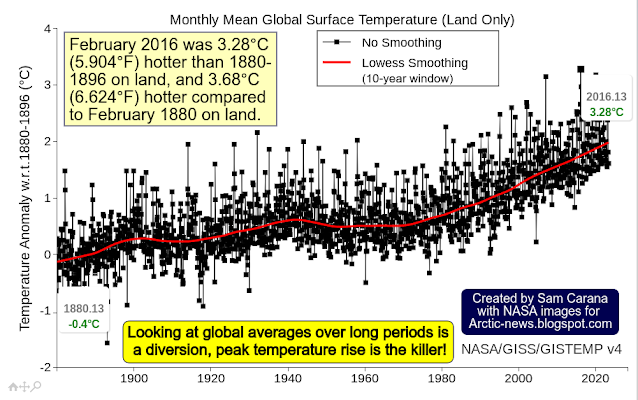
The 36-month running average for albedo (reflectivity) for May 2025 is down to a record low of 28.711%, as illustrated by the above Eliot Jacobson image.
The 36-month running mean for the Earth energy imbalance grew in May 2025 to 11.36 Hiroshimas per second. That's roughly 980,000 Hiroshimas per day in planetary warming, adds Eliot Jacobson.
 |
| [ NOAA ENSO outlook ] |
The current ENSO conditions also make it even more significant that the global sea ice area anomaly was 2.56 million km² below the 1981-2010 mean on July 30, 2025, a standard deviation of -4.33σ from 1981-2010.
Arctic sea ice volume was at a record daily low on August 3, 2025, as it has been for more than a year, as illustrated by the image below.
The image below shows Arctic sea ice concentration on August 3, 2025.
As the temperature of the water of the Arctic Ocean rises, more ocean heat can penetrate sediments at the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, which can destabilize methane hydrates contained in these sediments and cause eruptions of huge amounts of methane from the hydrates and from free gas kept underneath these hydrates.
The image below shows that methane concentrations as high as 2535 parts per billion (ppb) were recorded at a pressure level of 695.1 mb by the NOAA 20 satellite on July 30, 2025 AM. High concentrations of methane show up at latitudes higher than 30°N.
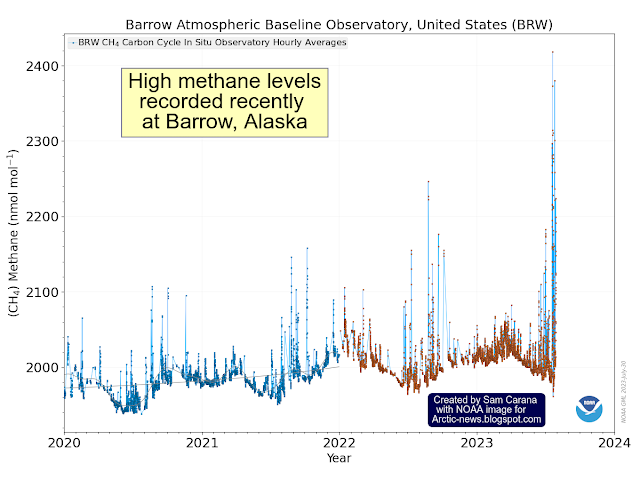
The image below shows hourly methane measurements taken at the Barrow Atmospheric Baseline Observatory (BRW), a NOAA facility located near Utqiaġvik (formerly Barrow), Alaska, at 71.32 degrees North.
 |
| [ from the post When will humans go extinct? ] |
 |
| [ from: When Will We Die? ] |
A 2018 study by Strona & Bradshaw indicates that most life on Earth will disappear with a 5°C rise (see box on the right). Humans, who depend on a lot of other species, will likely go extinct with a 3°C, as discussed in the earlier post When Will We Die?
Climate Emergency Declaration
The situation is dire and the precautionary principle calls for rapid, comprehensive and effective action to reduce the damage and to improve the situation, as described in this 2022 post, where needed in combination with a Climate Emergency Declaration, as discussed at this group.
Links
• Climate Reanalyzer
https://climatereanalyzer.org
• IPCC AR6 WG1 Figure 4.35 | Comparison of RCPs and SSPs
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/downloads/figures/IPCC_AR6_WGI_Figure_4_35.png
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/figures/chapter-4/figure-4-35
• Saltier water, less sea ice
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2025/07/saltier-water-less-sea-ice.html
• Nullschool.net
https://earth.nullschool.net
• Marine heatwaves as hot spots of climate change and impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem services - by Thomas Wernberg et al.
https://www.facebook.com/groups/arcticnews/posts/10162992131044679
• Copernicus
https://pulse.climate.copernicus.eu
• NASA - Ocean warming (December 2024)
https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/ocean-warming/?intent=121
• Arctic Blue Ocean Event 2025? (update June 2025)
• A 485-million-year history of Earth’s surface temperature - by Emily Judd et al. (2024)
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adk3705
https://www.facebook.com/groups/arcticnews/posts/10161741588279679
• Global warming in the pipeline - by James Hansen et al.
https://academic.oup.com/oocc/article/3/1/kgad008/7335889
https://www.facebook.com/groups/arcticnews/posts/10161110558744679
• Pre-industrial
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/pre-industrial.html
• NOAA - Climate Prediction Center - ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions
https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/lanina/enso_evolution-status-fcsts-web.pdf
• Danish Meteorological Institute - sea ice thickness and volume
• University of Bremen
https://seaice.uni-bremen.de/start
• Kevin Pluck - sea ice visuals
https://seaice.visuals.earth
• NOAA - satellite methane measurements
https://www.ospo.noaa.gov/products/atmosphere/soundings/heap/nucaps/new/nucaps_products.html
• NOAA - flask and station methane measurements
https://gml.noaa.gov/dv/iadv/index.php
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2022/10/transforming-society.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Climate Emergency Declaration
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climate-emergency-declaration.html