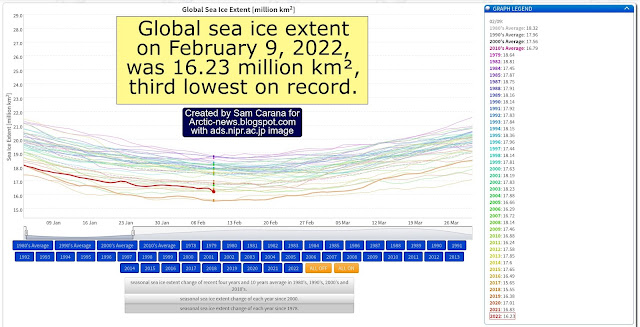
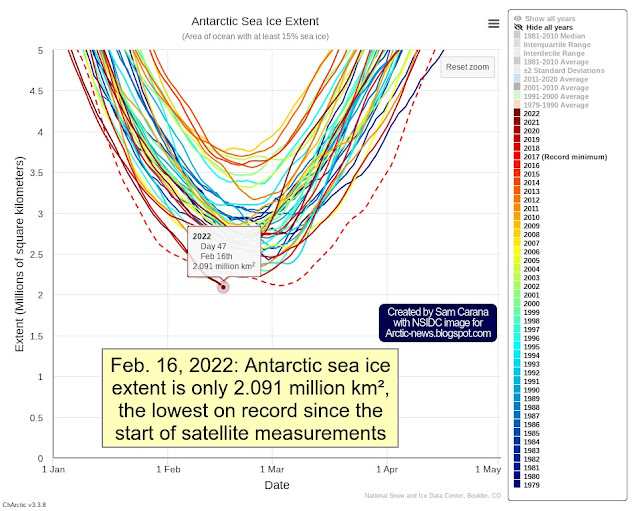
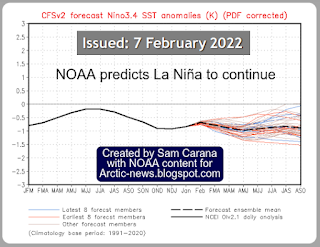
As above image shows, Antarctic sea ice extent was only 1.973 million km² on February 23, 2022, the lowest on record since satellite measurements began in 1979.
Earlier, on February 20, 2022, Antarctic sea ice extent was only 1.983 million km². On February 20, 2008, it was 3.783 million km². That's a difference of 1.8 million km², or some 0.36% of the total surface of Earth (which is 510,072,000 km²).
 |
| [ from the Albedo page ] |
Albedo refers to the reflectivity of the surface. Earth average albedo is 0.3 or 30%. The albedo of sea ice can be as high as 0.9 (i.e. 90% when covered with fresh snow). Currently, albedo of the sea ice is about 0.6 (the sea ice is partly covered with melt pools). Open water has an albedo of 0.06. So, disappearance of the sea ice makes an albedo difference of at least 0.5.
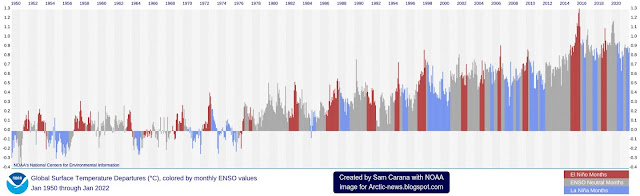
That's almost half as much as all human-caused global warming in 2019. As the image below shows, radiative forcing was 2.72 W/m² in 2019 relative to 1750, according to IPCC AR6.
• NSIDC - Charctic interactive Sea Ice Graph
https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/charctic-interactive-sea-ice-graph
• Wikipedia - Earth
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earth
• IPCC - Figure 2.11 (AR5/WG1/Chapter 2)
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/observations-atmosphere-and-surface/fig2-11_orig-pptx-2
• The global energy balance from a surface perspective - by Martin Wild et al. (2012)
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html