As climate change strikes with ever greater ferocity, five henchmen dominate the news: Storm, Flood, Heat, Smoke and Fire.
The image on the right shows very high temperatures over North America end July 2021, with fire radiative power as high as 247.3 MW.
The NASA Worldview satellite image below shows large smoke plumes on July 7, 2021, reaching Hudson Bay. Furthermore, large smoke plumes are also visible over British Columbia.
The NASA Worldview satellite image below shows smoke traveling from the West Coast to the East Coast of the U.S. on July 26, 2021.
The Copernicus image on the right shows Siberian fires spreading aerosols over the Arctic Ocean on August 2, 2021
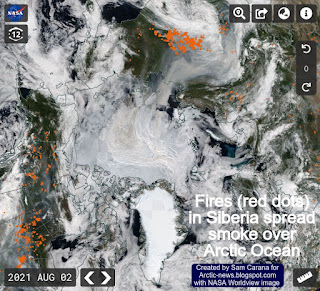
The NASA Worldview satellite image underneath on the right shows fires (red dots) in Siberia spreading smoke over the Arctic Ocean on August 2, 2021.
Mainstream media do cover such disasters, often with sensational footage and while pointing at the extensive damage and loss of life caused by such events.
However, mainstream media rarely point out that climate change is getting worse and and even more so due to feedbacks that can amplify extreme weather events and can further speed up how climate change unfolds.
One of these feedbacks is albedo loss, i.e. decline of the snow and ice cover resulting in less sunlight getting reflected back into space. Fires also come with soot that can settle on snow and ice, resulting in surface darkening that will speed up melting and albedo loss.
The rapid thinning of Arctic sea ice was discussed in an earlier post and is again illustrated by the image on the right.
The image shows the sea ice (or rather the lack of it) north of Greenland on August 15, 2021. This is where years ago the thickest sea ice was located. The melt season will continue for at least another month time, so the situation is very worrying, since the disappearance of the thicker sea ice means that the buffer is gone, i.e. that the latent heat tipping point of Arctic sea ice has been crossed.
Here's a link to compare the sea ice north of Greenland between July 29, 2021, and August 15, 2021.
NSIDC adds: The loss of the multiyear ice since the early 1980s started in earnest after the 2007 record low minimum sea ice cover that summer, and while there have been slight recoveries since then, it has not recovered to values seen in the 1980s, 1990s, or early 2000s. This loss of the oldest and thickest ice in the Arctic Ocean is one of the reasons why the summer sea ice extent has not recovered, even when weather conditions are favorable for ice retention.
The Naval Research Lab animation on the right shows Arctic sea ice thickness (in m) for the 30 days up to August 27, 2021, with eight days of forecasts included.
As the temperature difference between the North Pole and the Equator narrows, the wind flowing north on the Northern Hemisphere slows down, which changes the Jet Stream, resulting in more extreme weather events, including heatwaves and fires.
As the temperature difference between the North Pole and the Equator narrows, the wind flowing north on the Northern Hemisphere slows down, which changes the Jet Stream, resulting in more extreme weather events, including heatwaves and fires.
One of the most dangerous feedbacks is that, as temperatures of the water of the Arctic Ocean keeps rising, more heat will reach sediments under the Arctic Ocean where huge amounts of methane are stored, causing destabilization.
 |
| [ from the feedbacks page ] |
This destabilization threatens to cause huge quantities of methane to erupt and enter the atmosphere, as has been discussed in many earlier posts such as this one and this one.
This threat becomes dramatically larger as the latent heat threshold gets crossed and the buffer constituted by Arctic sea ice disappears, so further heat entering the Arctic Ocean from the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean can no longer be consumed in the process of melting the subsurface sea ice.
Ominously, the MetOp-2 satellite recorded a methane level of 2839 ppb at 469 mb on July 30, 2021 pm, as the image on the right shows.
The image underneath shows large quantities of methane over the East Siberian Arctic Shelf (ESAS) at 469 mb on August 4, 2021 pm.
On August 4, 2021, there still was some sea ice present in the ESAS. While this remaining sea ice does prevent a lot of sunlight from reaching the water and heating it up, the sea ice also acts as a seal, preventing ocean heat from getting transferred to the atmosphere. The water in the ESAS is very shallow, less than 50 meter in most places, which makes it easier for heat to reach sediments, while it also makes it harder for methane that is rising through the water column to get decomposed by microbes in the water.
On August 4, 2021, there still was some sea ice present in the ESAS. While this remaining sea ice does prevent a lot of sunlight from reaching the water and heating it up, the sea ice also acts as a seal, preventing ocean heat from getting transferred to the atmosphere. The water in the ESAS is very shallow, less than 50 meter in most places, which makes it easier for heat to reach sediments, while it also makes it harder for methane that is rising through the water column to get decomposed by microbes in the water.
 |
| [ large quantities of methane over ESAS ] |
The image underneath shows that on August 4, 2021 am, at 293 mb, the MetOp-1 satellite recorded a mean global methane level of 1942 ppb.
At a 1-year Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 200, this translates into 388.2 ppm CO₂e. By comparison, the CO₂ level on August 4, 2021, was 414.89 ppm according to the Keeling Curve measurements at Mauna Loa, Hawaii. A GWP of 200 for methane is appropriate in the light of the danger of a huge burst of methane erupting from the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, which would, due to the abrupt nature of such an eruption, make its impact felt instantaneously.
 |
| [ mean global methane level of 1941 ppb ] |
The situation is dire and calls for immediate, comprehensive and effective action as described in the Climate Plan.
Links
• Jet Stream
• Feedbacks
• NASA Worldview
• Copernicus - aerosols
• MetOp methane levels
• NSIDC: Arctic Sea Ice News & Analysis - August 18, 2021
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2021/06/heatwaves-and-the-danger-of-the-arctic-ocean-heating-up.html
• Arctic sea ice disappearing fast
• When will we die?
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2019/07/most-important-message-ever.html
• Confirm Methane's Importance
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2021/03/confirm-methanes-importance.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Confirm Methane's Importance
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2021/03/confirm-methanes-importance.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html