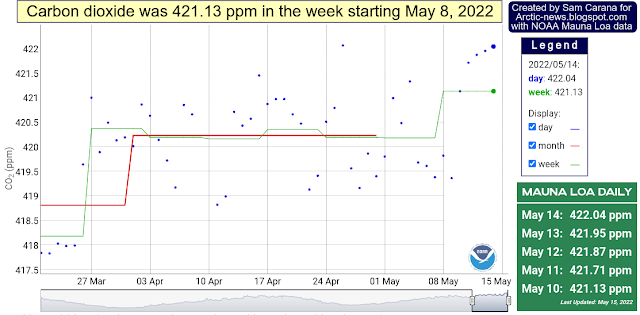
NOAA data show a carbon dioxide level of 421.13 parts per million (ppm) for the week starting May 8, 2022, a new record high since measurements started at Mauna Loa, Hawaii. As the image below also shows, very high daily levels were reached recently, as high as 422.04 ppm.
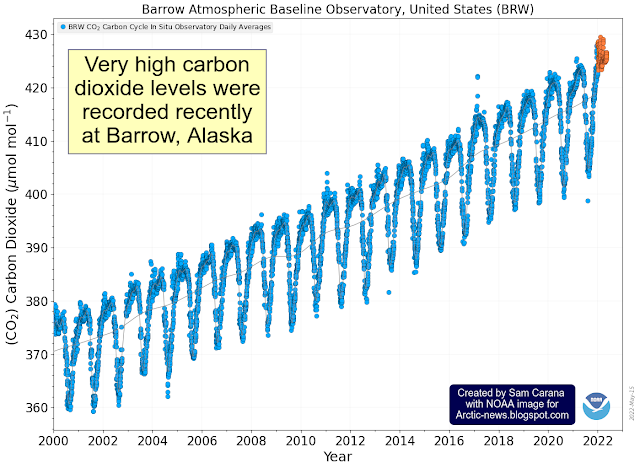
Greenhouse gas levels are even higher further north. Very high carbon dioxide levels were recorded recently at Barrow, Alaska, approaching 430 ppm.
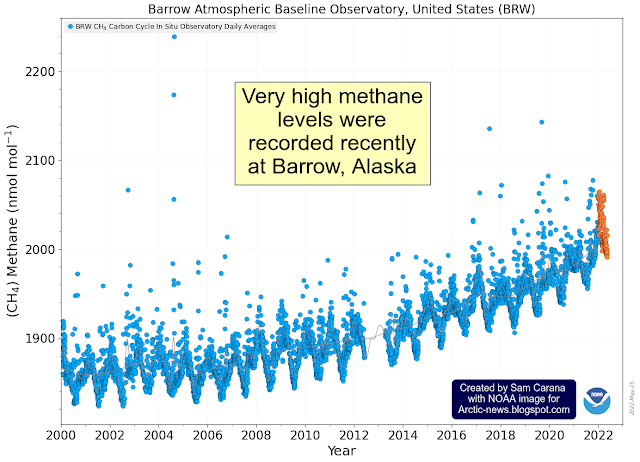
Furthermore, very high methane levels were recorded recently at Barrow, Alaska, including many at levels well over 2000 parts per billion (ppb).
The trigger: El Niño and sunspots
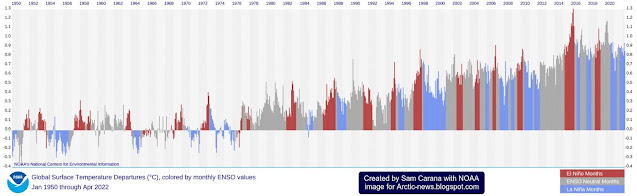
El Niños typically occur every 3 to 5 years, according to NOAA and as illustrated by the NOAA image below, so the upcoming El Niño can be expected to occur within the next few years.
As also illustrated by the NOAA image on the right, we are currently in the depths of a persistent La Niña and this suppresses current temperatures.
A huge temperature rise in the Arctic looks set to unfold soon, triggered by the combined impact of an upcoming El Niño and a peak in sunspots.
Sunspots are currently well above what NOAA predicted, as illustrated by the image below on the right.
Huge temperature rise in Arctic
Additionally, greenhouse gas levels are very high over the Arctic, while the ocean heat that enters the Arctic Ocean from the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean keeps rising.
As temperatures keep rising in the Arctic, changes to the Jet Stream look set to intensify, while loss of terrestrial albedo in the Arctic could equal the albedo loss resulting from sea ice decline.
Further feedbacks include permafrost degradation, both terrestrial and on the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, which looks set to cause huge releases of greenhouse gases (particularly CO₂, CH₄ and N₂O).
https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends
• NOAA - Global Monitoring Laboratory, at Barrow, Alaska, U.S.
https://gml.noaa.gov/dv/iadv/graph.php?code=BRW&program=ccgg&type=ts
• Arctic Hit By Ten Tipping Points
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2020/04/arctic-hit-by-ten-tipping-points.html
• NOAA - El Niño
https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource-collections/weather-atmosphere/el-nino#:~:text=An%20El%20Ni%C3%B1o%20condition%20occurs,every%203%20to%205%20years.
• NOAA - Monthly Temperature Anomalies Versus El Niño
 |
| [ from the Extinction page ] |
Further feedbacks include permafrost degradation, both terrestrial and on the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, which looks set to cause huge releases of greenhouse gases (particularly CO₂, CH₄ and N₂O).
Global temperature rise
This would in turn also cause more water vapor to enter the atmosphere, further speeding up the temperature rise, especially in the Arctic, where vast amounts of methane are contained in sediments at the seafloor and where there is very little hydroxyl in the air to break down the methane.
Temperatures looks set to rise further due to the falling away of sulfate aerosols, while there could be a further temperature rise due to releases of other aerosols that have a net warming impact, such as black and brown carbon, which can increase dramatically as more wood burning and forest fires take place.
As the temperature keeps rising, further self-reinforcing feedbacks will kick in with more ferocity such as an increase in water vapor globally combined with a decrease in lower clouds decks, further increasing the temperature, as described at the clouds feedback page.
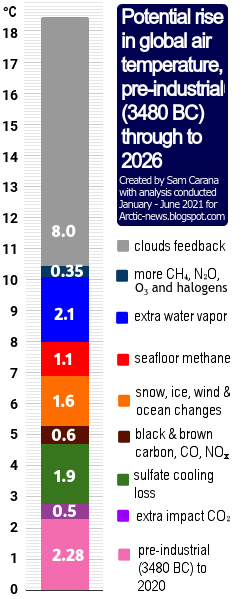
Altogether, the global temperature could rise by more than 18°C above pre-industrial, as illustrated by the image on the right from the Extinction page.
Conclusion
In conclusion, temperatures could rise strongly by 2026, resulting in humans going extinct, making it in many respects rather futile to speculate about what will happen beyond 2026.
At the same time, the right thing to do is to help avoid the worst things from happening, through comprehensive and effective action as described in the Climate Plan.
Links
• NOAA - Global Monitoring Laboratory, Recent Daily
Average CO₂ at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, U.S. Temperatures looks set to rise further due to the falling away of sulfate aerosols, while there could be a further temperature rise due to releases of other aerosols that have a net warming impact, such as black and brown carbon, which can increase dramatically as more wood burning and forest fires take place.
As the temperature keeps rising, further self-reinforcing feedbacks will kick in with more ferocity such as an increase in water vapor globally combined with a decrease in lower clouds decks, further increasing the temperature, as described at the clouds feedback page.
Altogether, the global temperature could rise by more than 18°C above pre-industrial, as illustrated by the image on the right from the Extinction page.
Conclusion
In conclusion, temperatures could rise strongly by 2026, resulting in humans going extinct, making it in many respects rather futile to speculate about what will happen beyond 2026.
At the same time, the right thing to do is to help avoid the worst things from happening, through comprehensive and effective action as described in the Climate Plan.
Links
• NOAA - Global Monitoring Laboratory, Recent Daily
https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends
• NOAA - Global Monitoring Laboratory, at Barrow, Alaska, U.S.
https://gml.noaa.gov/dv/iadv/graph.php?code=BRW&program=ccgg&type=ts
• Arctic Hit By Ten Tipping Points
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2020/04/arctic-hit-by-ten-tipping-points.html
• NOAA - El Niño
https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource-collections/weather-atmosphere/el-nino#:~:text=An%20El%20Ni%C3%B1o%20condition%20occurs,every%203%20to%205%20years.
• NOAA - Monthly Temperature Anomalies Versus El Niño
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/monthly-report/global/202204/supplemental/page-4
• Sunspots
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/sunspots.html
• Sunspots
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/sunspots.html
• NOAA - sunspots
• Latent heat
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/latent-heat.html
• Blue Ocean Event
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/blue-ocean-event.html
• Feedbacks
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/feedbacks.html
• Aerosols
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/aerosols.html
• Clouds feedback and tipping point
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/clouds-feedback.html
• Jet Stream
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/jet-stream.html
• The Importance of Methane
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/the-importance-of-methane-in-climate.html
• When Will We Die?
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2019/06/when-will-we-die.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Feedbacks
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/feedbacks.html
• Aerosols
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/aerosols.html
• Clouds feedback and tipping point
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/clouds-feedback.html
• Jet Stream
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/jet-stream.html
• The Importance of Methane
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/the-importance-of-methane-in-climate.html
• When Will We Die?
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2019/06/when-will-we-die.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html