|
| [ click on images to enlarge ] |
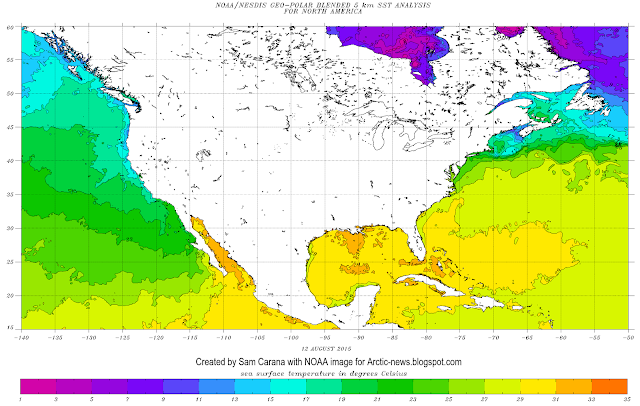
As the top image shows, sea surface temperature anomalies in the Bering Strait on August 4, 2015, were as high as 8.7°C (15.6°F). Such high anomalies are caused by a combination of ocean heat, of heatwaves over Alaska and Siberia extending over the Bering Strait, and of warm river water run-off.
As the image on the right shows, sea surface temperatures in the Bering Strait were as high as 20.5°C (69.1°F) on August 4, 2015.
As warm water flows through the Bering Strait into the Arctic Ocean, it dives under the sea ice and becomes harder to detect by satellites that typically measure water temperatures at the surface, rather than below the surface.
The image below shows sea surface temperature anomalies from 1971 to 2000, for August 6, 2015, as visualized by Climate Reanalyzer.
Climate Reanalyzer applies a mask over sea-ice-covered gridcells, reducing anomalies in such cells to zero.
Below is a NOAA image, for August 5, 2015, also with anomalies from 1971 to 2000.
Below is another NOAA image, showing anomalies for August 6, 2015. Because the base period is 1961 to 1990, the anomalies are higher. Nonetheless, the yellow areas that feature around the North Pole on above image do not show up on the image below.
In other words, looking at sea surface temperatures alone may lead to underestimations of the temperatures of the water underneath the sea ice. Keeping that in mind, have a look again at the high anomalies on the image below.
The danger is that further decline of the sea ice will lead to rapid warming of the Arctic Ocean, while the presence of more open water will also increase the opportunity for strong storms to develop that can mix high sea surface temperatures all the way down to the seafloor, resulting in destabilization of sediments and triggering releases of methane that can be contained in such sediments in huge amounts.
The image below shows that global mean methane levels as high as 1840 parts per billion (ppb) were recorded on August 4, 2015. Peak methane levels that day were as high as 2477 ppb.
This peak level of 2477 ppb isn't the highest recorded the year. As the image below shows and as discussed in a
previous post, methane levels as high as 2845 ppb were recorded on April 25, 2015. The average of the daily peaks for this year up to now is 2355 ppb. Very worrying about the above image are the high levels of methane showing up over the Arctic Ocean.
As above image also shows, the mean methane level of 1840 ppb is in line with expectations, as methane levels rise over the course of the year, to reach a maximum in September. This mean level of 1840 ppb is higher than any mean level since records began.
The image below shows all the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) annual means that are available, i.e. for the period 1984 through to 2013.
As above image shows, a polynomial trendline based on these WMO data (for the period 1984 through to 2013) points at a doubling of mean global methane levels by about 2040. The added NOAA data are the highest mean in 2014, i.e. 1839 ppb recorded on September 7, 2014, and the above-mentioned level of 1840 ppb recorded on August 4, 2015.

As said, mean global methane levels last year reached its peak in September and the same is likely to occur this year. In other words, this new record is likely to be superseded by even higher levels soon.
The image on the right shows the steady rise of the highest mean daily methane levels that have been recorded recently, indicating that a continued rise can be expected that would put another highest mean level for 2015 on the trendline of above image soon.
Again, the danger is that a warming Arctic Ocean will trigger further methane releases from the seafloor, leading to rapid local warming that in turn will trigger further methane releases, in a vicious cycle of runway warming.

As illustrated by the image on the right, at a 10-year timescale, the current global release of methane from all anthropogenic sources exceeds all anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions as agents of global warming.
Over the next decade or so, methane emissions are already now more important than carbon dioxide emissions in driving the rate of global warming, and this situation looks set to get worse fast.
Unlike carbon dioxide, methane's GWP does rise as more of it is released. Higher methane levels cause depletion of hydroxyl, which is the main way for methane to be broken down in the atmosphere.
The situation is dire and calls for comprehensive and effective action as discussed at the
Climate Plan.
The image shows all the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) annual means that are available, i.e. for the period...
Posted by Sam Carana on Friday, August 7, 2015