“The 1st Law of Humanity: Don’t kill your children!”
(Hans Joachim Schellnhuber, chief climate advisor to the German Government).
http://www.pik-potsdam.de/news/inshort/files/Schellnhuber-keynote-COP18-state-dinner-Doha.pdf
“Earth is worth £3,000 trillion, according to scientist's new planet valuing formula”
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1361145/Earth-worth-3-000-trillionaccording-scientists-new-planet-valuing-formula.html
 |
| Earth rising over the Moon - http://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/features/bm_gallery_4.html |
That people can be duped to accept the destruction of the atmosphere – the lungs of the biosphere - is something no science-fiction has yet described, yet, as the summary of the scientific evidence presented below indicates, is now science-fact.
By the end of the 20th century powerful vested interests, including corporations and few billionaires and their political mouthpieces, combined to promote saturation of the terrestrial atmosphere with carbon dioxide, in contravention of climate science, are experiencing a Pyrrhic victory oblivious to the unfolding tragedy.
Nothing exemplifies these developments more than the current Australian elections. An internet search for the terms ‘Australia’ ‘elections’ and ‘climate change’ recovers very little in terms of party policies
(http://theconversation.com/why-labor-should-fight-the-2013-election-on-climate-change-13865, http://www.theguardian.com/environment/southerncrossroads/2013/aug/05/australian-election-2013-climate-change).
For example, the words ‘climate change’ (or ‘global warming’) were not even mentioned in a recent ABC prime time QandA pre-election program, in which the opposition shadow environmental minister participated. A cosmetic carbon price is threatened by the largest party, nor do many refer to Australia being on track to become an equivalent of Saudi Arabia in terms of global fossil fuel (coal) exports.
Featuring heavily in the current election campaign are the potential financial debts of future generations but little is said about the environmental debt – life under 4 degrees Celsius (above pre-industrial temperatures). Only a minor party is focused on the climate calamity.
When the theory of ‘economic rationalism’ emerged, pricing every item including cultural and spiritual values, a question arose as to “The price of the Earth”, currently estimated as 3000 trillion pounds (http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1361145/Earth-worth-3-000-trillion-according-scientists-new-planet-valuing-formula.html).
A Faustian Bargain is on (http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dr-james-hansen/doubling-down-on-our-faustian-bargain_b_2989535.html). What commenced some 20 years ago as a scientific debate has deteriorated to media-dominated pseudo-debate replete with misrepresentations of the science. Below I highlight the principal line of evidence emerging from geological and paleoclimate science:
Critical to the evolution of life since at least ~3.5 billion years-ago, from where the earliest known stromatolites and micro-fossils are recorded [1], are the combined effects of solar insolation and atmospheric chemistry, which control temperatures (-90° to +58°C) and the state of H2O at the surface as vapor, ice or liquid – the latter allowing life. Compensating for the continuous release of CO2 from the crust and mantle by volcanic eruption are tectonic, weathering and sedimentary processes that recycle the crust and lock CO2 in carbonates and organic matter subducted into the mantle [2], preventing a run-away build-up of atmospheric greenhouse gases (the Venus syndrome [3]).
The histories of the atmosphere, the oceans and life are thus closely intertwined. The atmosphere, mediating the carbon, oxygen and nitrogen cycles (see above image), acting as the lungs of the biosphere, regulates an aqueous medium where microbiological metabolic processes occur, from chemo-bacteria around volcanic fumaroles, to nanobes in deep crustal fractures, to nearsurface phototrophs. From ~420 million years ago the advent of land plants ensued in flammable carbon-rich land surfaces interfaced with an oxygen rich atmosphere, ensuing in a combustible combination [4]. Repeatedly through geological history volcanic eruptions and asteroid impacts triggered major release of greenhouse gases (GHG) from the crust as well as extensive surface fires, major climate changes and mass extinctions of species [5].
The current rise of atmospheric GHG at an unprecedented rate (see above image), defines the Anthropocene [6] as an oxidation event, a new geological era triggered by a species which has uniquely mastered ignition, excavating and releasing hundreds of billions of tons (more than 560 GtC) of carbon from geological formations into atmosphere. The consequences for the biosphere, referred to as the 6th mass extinction of species [7], are leading to a tragedy for human ideals and for nature.
Is the Anthropocene event horizon a purely pre-determined natural? Alternatively, where does responsibility lie?
On the scale of the species, once the energy output of the genus Homo was magnified through combustion by many orders of magnitude, the phenomenon can be deemed an inherent part of natural evolution. This may lead to a deterministic conclusion: It is unlikely to expect any species to be as perfectly wise and responsible as to be able to constrain the effects of its invention.
Where does free will lie? On the scale of modern civilization, since the greenhouse effect [8] and its underlying laws of physics and chemistry [9] have been identified in the 19th century, the question arises to what extent would societies and their leaders accept the implications of the science for human industry? Will the scientific method itself and the enlightenment [10] form the basis of future decisions?
In so far as government and corporate decisions are influenced by misconceptions and misrepresentations of the science, as an excuse for inaction, responsibility for the rapidly unfolding shift in the state of the terrestrial climate lies with the shortsightedness of Homo sapiens.
It is the peer review system which forms the venue for science communications. However, toward the end of the 20th century a multitude of media pieces and hundreds of websites began proliferate pseudoscience notions ignorant of the principles of science in general and of climate science in particular. Nor, in general, were practicing climate scientists allowed the same access to the popular media to communicate their research, a situation aggravated by conspiracy theories and ad-hominem aimed against climate scientists.
The lesson of numerous attempted debates since 2005 with those who deny the reality of global warming, or attempt to attribute it to natural non-human factors, show these notions cannot be dissuaded by any amount of evidence [11, 12, 13]. Numerous erroneous claims continue to be made. To cite just a few examples:
References
For example, the words ‘climate change’ (or ‘global warming’) were not even mentioned in a recent ABC prime time QandA pre-election program, in which the opposition shadow environmental minister participated. A cosmetic carbon price is threatened by the largest party, nor do many refer to Australia being on track to become an equivalent of Saudi Arabia in terms of global fossil fuel (coal) exports.
Featuring heavily in the current election campaign are the potential financial debts of future generations but little is said about the environmental debt – life under 4 degrees Celsius (above pre-industrial temperatures). Only a minor party is focused on the climate calamity.
When the theory of ‘economic rationalism’ emerged, pricing every item including cultural and spiritual values, a question arose as to “The price of the Earth”, currently estimated as 3000 trillion pounds (http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1361145/Earth-worth-3-000-trillion-according-scientists-new-planet-valuing-formula.html).
A Faustian Bargain is on (http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dr-james-hansen/doubling-down-on-our-faustian-bargain_b_2989535.html). What commenced some 20 years ago as a scientific debate has deteriorated to media-dominated pseudo-debate replete with misrepresentations of the science. Below I highlight the principal line of evidence emerging from geological and paleoclimate science:
Critical to the evolution of life since at least ~3.5 billion years-ago, from where the earliest known stromatolites and micro-fossils are recorded [1], are the combined effects of solar insolation and atmospheric chemistry, which control temperatures (-90° to +58°C) and the state of H2O at the surface as vapor, ice or liquid – the latter allowing life. Compensating for the continuous release of CO2 from the crust and mantle by volcanic eruption are tectonic, weathering and sedimentary processes that recycle the crust and lock CO2 in carbonates and organic matter subducted into the mantle [2], preventing a run-away build-up of atmospheric greenhouse gases (the Venus syndrome [3]).
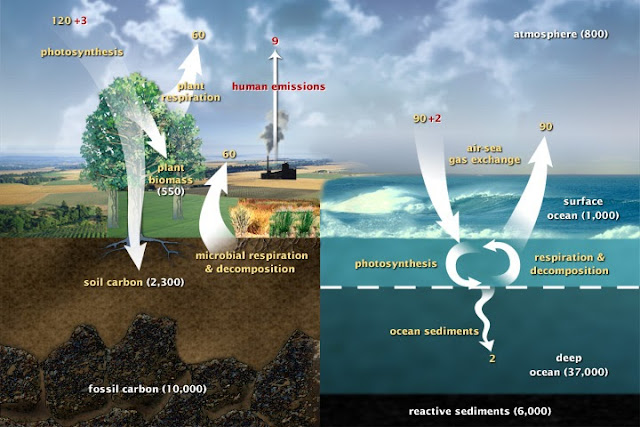 |
| Movement of carbon between land, atmosphere, and oceans in billions of tons of carbon per year. Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, red are human contributions in billions of tons of carbon per year. White numbers indicate stored carbon. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_cycle |
The current rise of atmospheric GHG at an unprecedented rate (see above image), defines the Anthropocene [6] as an oxidation event, a new geological era triggered by a species which has uniquely mastered ignition, excavating and releasing hundreds of billions of tons (more than 560 GtC) of carbon from geological formations into atmosphere. The consequences for the biosphere, referred to as the 6th mass extinction of species [7], are leading to a tragedy for human ideals and for nature.
Is the Anthropocene event horizon a purely pre-determined natural? Alternatively, where does responsibility lie?
On the scale of the species, once the energy output of the genus Homo was magnified through combustion by many orders of magnitude, the phenomenon can be deemed an inherent part of natural evolution. This may lead to a deterministic conclusion: It is unlikely to expect any species to be as perfectly wise and responsible as to be able to constrain the effects of its invention.
Where does free will lie? On the scale of modern civilization, since the greenhouse effect [8] and its underlying laws of physics and chemistry [9] have been identified in the 19th century, the question arises to what extent would societies and their leaders accept the implications of the science for human industry? Will the scientific method itself and the enlightenment [10] form the basis of future decisions?
In so far as government and corporate decisions are influenced by misconceptions and misrepresentations of the science, as an excuse for inaction, responsibility for the rapidly unfolding shift in the state of the terrestrial climate lies with the shortsightedness of Homo sapiens.
It is the peer review system which forms the venue for science communications. However, toward the end of the 20th century a multitude of media pieces and hundreds of websites began proliferate pseudoscience notions ignorant of the principles of science in general and of climate science in particular. Nor, in general, were practicing climate scientists allowed the same access to the popular media to communicate their research, a situation aggravated by conspiracy theories and ad-hominem aimed against climate scientists.
The lesson of numerous attempted debates since 2005 with those who deny the reality of global warming, or attempt to attribute it to natural non-human factors, show these notions cannot be dissuaded by any amount of evidence [11, 12, 13]. Numerous erroneous claims continue to be made. To cite just a few examples:
- The claim, as if temperature rise preceded CO2 rise during the glacial terminations therefore the current rise of temperature is not the result of CO2 rise [14], cannot be sustained. The effects of CO2 and temperature variations are intertwined. During the last ~400,000 years glacial eras were terminated by solar maxima, affecting decreased CO2 solubility in warming water and thereby a rise in CO2 levels of the atmosphere. By contrast climate developments since the 18th century, when negligible or no rise in insolation occurred, were triggered by the anthropogenic greenhouse effect of the release of >560 billion ton carbon, consistent with the basic laws of physics [9].
- The claim as if global warming represents recovery from the ‘Little Ice Age’ (LIA) cannot be sustained: The LIA was caused by a near-cessation of sunspot activity during ~1650-1700, depressing global temperatures by ~0.2-0.3°C relative to preceding periods. By contrast, following a lull, global warming from about 1975 tracked toward more than 1.5°C over the continents relative to pre-industrial temperatures [15].
- Claims related to the cosmic rays flux (CRF) effects: A dominant solar effect on the climate since 1970 is ruled out by measurements of solar radiation [16]. The incidence of cosmic rays, which oscillate reciprocally with the 11 years sunspot cycle, has been shown to have minor effects on cloud nucleation and has not varied significantly since the mid-20th century [17].
- The claim as if carbon dioxide is emitted mainly from volcanoes: According to the United States Geological Survey (2012) sub-aerial and sub-marine volcanism emits approximately 150 – 260 million tons CO2 per-year whereas anthropogenic emissions total about 35 billion tons CO2/per-year [18].
- Mars warming [19]: The argument invokes unknown solar system-wide phenomena, despite measurements of solar radiation and the cosmic ray flux which show little change since the mid-20th century. Some temperature fluctuations in Mars are known to be related to dust storms.
References
- http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v441/n7094/abs/nature04764.html
- http://www.platetectonics.com/book/page_12.asp
http://www.columbia.edu/~vjd1/carbon.htm - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Runaway_greenhouse_effect
- http://www.sciencemag.org/content/324/5926/481.abstract
- http://www.skepticalscience.com/Earths-five-mass-extinction-events.html
- http://rsta.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/369/1938/842.abstract
- http://edition.cnn.com/2002/TECH/science/08/23/green.century.mass.extinction/index.html
- http://www.aip.org/history/climate/co2.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
- http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/enlightenment/
- http://www.bookdepository.com/Merchants-of-Doubt-NaomiOreskes/9781608193943?redirected=true&gclid=CPe3uYiZ4bgCFUpZpQodIhcAvQ
- http://www.amazon.com/Climate-Change-Denial-Heads-Sand/dp/1849713367
- http://www.amazon.com/A-Short-Introduction-Climate-Change/dp/11076187625
- http://www.skepticalscience.com/co2-lags-temperature.htm
- http://berkeleyearth.org/
- http://www.mps.mpg.de/homes/natalie/PAPERS/warming.pdf
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X06004328 - http://www.pik-potsdam.de/~stefan/Publications/Journals/rahmstorf_etal_eos_2004.html http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364682603000415
- http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/hazards/gas/climate.php
- http://www.skepticalscience.com/global-warming-on-mars.htm
- http://www.miningaustralia.com.au/news/coal-mining-has-a-future-combet
- http://www.pik-potsdam.de/news/press-releases/4-degrees-briefing-for-the-world-bank-therisks-of-a-future-without-climate-policy
http://www.spiegel.de/international/world/merkelclimate-advisor-blasts-politicians-for-doing-too-little-a-868024.html
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/11/121119104842.htm - http://www.nature.com/nclimate/journal/v2/n7/full/nclimate1452.html
http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2012/07/30/1205276109.full.pdf+html
http://www.realclimate.org/index.php/archives/2012/08/extreme-metrics/
http://www.aph.gov.au/parliamentary_business/committees/senate_committees?url=ec_ctte/extreme_weather/index.htm - http://blog.ucsusa.org/bigger-hotter-and-longer-wildfires-are-the-new-normal-as-theclimate-changes-in-the-west-183


















