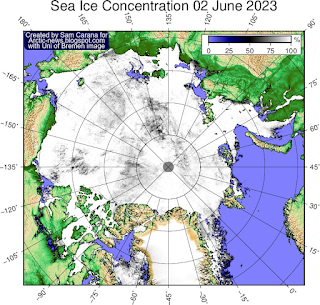
The image below illustrates the decline of Arctic sea ice volume over the years. The image also confirms that the annual maximum volume was recently reached and that it was the lowest maximum for the 24 years on record.
Given that Arctic sea ice currently is still relatively extensive, this record low volume indicates that sea ice is indeed very thin, which must be caused by ocean heat melting sea ice from below, since little or no sunshine is yet reaching the Arctic at the moment and air temperatures are still far below freezing point, so where ocean heat may be melting sea ice away from below, a thin layer of ice will quickly be reestablished at the surface, keeping sea ice extent relatively large for now.
This situation looks set to dramatically change over the next few months, as air temperatures will rise and as more ocean heat will reach the Arctic Ocean. Moreover, as illustrated by the map below, much of the thicker sea ice is located off the east coast of Greenland. This sea ice and the purple-colored sea ice can be expected to melt away quickly with the upcoming rise in temperatures over the next few months.
The image below, created with Climate Reanalyzer screenshots, shows that the sea surface temperature (SST 60°S - 60°N mean) was 21.2°C on April 24, 2024, reaching yet another record high.
These record high sea surface temperatures are reached as long-term sea surface temperatures are falling and as El Niño is predicted to weaken, which is fueling fears that feedbacks are kicking in with accelerating ferocity.
The image below, adapted from NOAA, shows global ocean temperature anomalies from 1901-2000, with the green line (LOcally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing) giving a warning that higher temperature anomalies could be coming up.
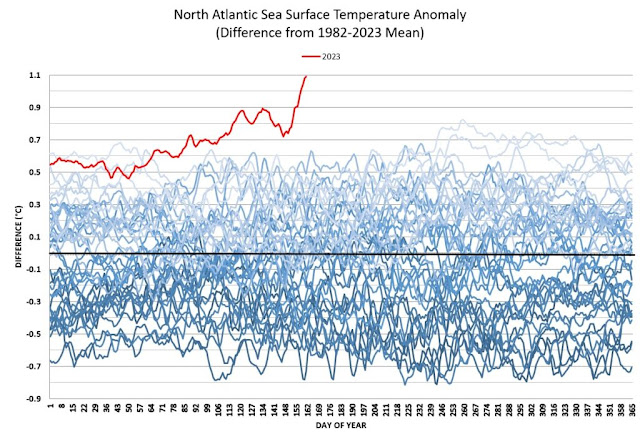
The image below shows that the monthly Atlantic surface temperature anomaly in March 2024 was 1.422°C when compared to a 1901-2000 base.
The high anomalies over the past two months indicate how much heat has accumulated in the Atlantic, and these anomalies are even higher when using a pre-industrial base, as discussed earlier.
The images also highlight the potential for the slowing down of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) to contribute to more heat accumulating at the surface of the Atlantic Ocean.
Arctic sea ice under threat
As temperatures rise, many feedbacks are kicking in with greater ferocity, including increased stratification of oceans, loss of sea ice, loss of reflectivity of clouds and increased freshwater due to stronger melting of sea ice and glacial ice, due to heavier runoff from land and rivers and due to changes in ocean circulation.
While this may look to cause less ocean heat to reach the Arctic Ocean for now, the result is that a huge amount of ocean heat is accumulating in the North Atlantic that threatens to abruptly move into the Arctic Ocean. The danger is that an influx of ocean heat can cause large amounts of methane to erupt from the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean.
An enormous amount of ocean heat has accumulated and is still further accumulating in the North Atlantic and much of this heat threatens to abruptly move into the Arctic Ocean. The danger is that, due to strong wind along the path of the Gulf Stream and extensions of this current into the Arctic Ocean, huge amounts of ocean heat will abruptly get pushed into the Arctic Ocean, with the influx of ocean heat causing destabilization of hydrates contained in sediments at the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, resulting in eruptions of huge amounts of methane.
The danger is growing, due to a number of factors. Firstly, the amount of ocean heat in the North Atlantic is increasing. Secondly, Arctic sea ice volume is at record low, implying that there is little or no buffer left to consume ocean heat flowing from the Atlantic Ocean into the Arctic Ocean.
Latent heat is energy associated with a phase change, such as the energy consumed when solid ice turns into water (i.e. melts). During a phase change, the temperature remains constant. Sea ice acts as a buffer that absorbs heat, while keeping the temperature at zero degrees Celsius. As long as there is sea ice in the water, this sea ice will keep absorbing heat, so the temperature doesn't rise at the sea surface.
 |
| [ image from earlier post ] |
These record high sea surface temperatures are reached as long-term sea surface temperatures are falling and as El Niño is predicted to weaken, which is fueling fears that feedbacks are kicking in with accelerating ferocity.
The image below, adapted from NOAA, shows global ocean temperature anomalies from 1901-2000, with the green line (LOcally Estimated Scatterplot Smoothing) giving a warning that higher temperature anomalies could be coming up.
 |
| [ image from earlier post ] |
The image below shows that the monthly Atlantic surface temperature anomaly in March 2024 was 1.422°C when compared to a 1901-2000 base.
The high anomalies over the past two months indicate how much heat has accumulated in the Atlantic, and these anomalies are even higher when using a pre-industrial base, as discussed earlier.
The images also highlight the potential for the slowing down of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) to contribute to more heat accumulating at the surface of the Atlantic Ocean.
Arctic sea ice under threat
As temperatures rise, many feedbacks are kicking in with greater ferocity, including increased stratification of oceans, loss of sea ice, loss of reflectivity of clouds and increased freshwater due to stronger melting of sea ice and glacial ice, due to heavier runoff from land and rivers and due to changes in ocean circulation.
While this may look to cause less ocean heat to reach the Arctic Ocean for now, the result is that a huge amount of ocean heat is accumulating in the North Atlantic that threatens to abruptly move into the Arctic Ocean. The danger is that an influx of ocean heat can cause large amounts of methane to erupt from the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean.
An enormous amount of ocean heat has accumulated and is still further accumulating in the North Atlantic and much of this heat threatens to abruptly move into the Arctic Ocean. The danger is that, due to strong wind along the path of the Gulf Stream and extensions of this current into the Arctic Ocean, huge amounts of ocean heat will abruptly get pushed into the Arctic Ocean, with the influx of ocean heat causing destabilization of hydrates contained in sediments at the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, resulting in eruptions of huge amounts of methane.
The danger is growing, due to a number of factors. Firstly, the amount of ocean heat in the North Atlantic is increasing. Secondly, Arctic sea ice volume is at record low, implying that there is little or no buffer left to consume ocean heat flowing from the Atlantic Ocean into the Arctic Ocean.
Latent heat is energy associated with a phase change, such as the energy consumed when solid ice turns into water (i.e. melts). During a phase change, the temperature remains constant. Sea ice acts as a buffer that absorbs heat, while keeping the temperature at zero degrees Celsius. As long as there is sea ice in the water, this sea ice will keep absorbing heat, so the temperature doesn't rise at the sea surface.
The amount of energy absorbed by melting ice is as much as it takes to heat an equivalent mass of water from zero to 80°C.
The danger is that, as the buffer disappears that until now has consumed huge amounts of ocean heat, further heat will reach methane hydrates at the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, causing them to get destabilized resulting in release of methane from these hydrates and from free gas underneath that was previously sealed by the hydrates.
Strong hurricanes can significantly add to the danger. More hurricanes are forecast for the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season than during 1950-2020, as illustrated by the image below, from an earlier post.
Many of the dangers have been discussed in earlier posts, e.g. the danger that sea currents in the Arctic Ocean will change direction was discussed in this 2017 post.
Climate Emergency Declaration
The situation is dire and the precautionary principle calls for rapid, comprehensive and effective action to reduce the damage and to improve the situation, as described in this 2022 post, where needed in combination with a Climate Emergency Declaration, as discussed at this group.
Links
• Climate Reanalyzer
https://climatereanalyzer.org
• NOAA - Ocean temperature anomalies
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series/globe/ocean/1/0/2015-2024?filter=true&filterType=loess
• Atlantic ocean heat threatens to unleash methane eruptions
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2024/03/atlantic-ocean-heat-threatens-to-unleash-methane-eruptions.html
• Feedbacks in the Arctic
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/feedbacks.html
• North Atlantic heating up
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2024/04/north-atlantic-heating-up.html
• Danish Meteorological Institute - Arctic sea ice thickness and volume
https://ocean.dmi.dk/arctic/icethickness/thk.uk.php
• Transforming Society
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2022/10/transforming-society.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Climate Emergency Declaration
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climate-emergency-declaration.html
 |
| [ The Buffer has gone, feedback #14 on the Feedbacks page ] |
Many of the dangers have been discussed in earlier posts, e.g. the danger that sea currents in the Arctic Ocean will change direction was discussed in this 2017 post.
Climate Emergency Declaration
The situation is dire and the precautionary principle calls for rapid, comprehensive and effective action to reduce the damage and to improve the situation, as described in this 2022 post, where needed in combination with a Climate Emergency Declaration, as discussed at this group.
Links
• Climate Reanalyzer
https://climatereanalyzer.org
• NOAA - Ocean temperature anomalies
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series/globe/ocean/1/0/2015-2024?filter=true&filterType=loess
• Atlantic ocean heat threatens to unleash methane eruptions
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2024/03/atlantic-ocean-heat-threatens-to-unleash-methane-eruptions.html
• Feedbacks in the Arctic
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/feedbacks.html
• North Atlantic heating up
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2024/04/north-atlantic-heating-up.html
• Danish Meteorological Institute - Arctic sea ice thickness and volume
https://ocean.dmi.dk/arctic/icethickness/thk.uk.php
• Transforming Society
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/2022/10/transforming-society.html
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Climate Emergency Declaration
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climate-emergency-declaration.html