by Andrew Glikson
In his book ‘
Collapse’ (2011) Jared Diamond portrays the fate of societies which Choose to Fail or Succeed. On a larger scale the
Fermi’s paradox suggests that advanced technological civilizations may constitute ephemeral entities in the galaxy, destined to collapse over short periods. Such an interpretation of Fermi’s paradox, corroborated by recent terrestrial history, implies that the apparent absence of
radio signals from Milky Way planets and beyond may be attributed to an inherently self-destructive nature of civilizations which reached the ability to propagate radio waves, consistent with
Carl Sagan’s views. It can be expected therefore that the number of advanced technological societies in the universe will be
proportional to their average lifetime, perhaps lasting no more than a few centuries. Inexplicably, the behavior of Homo “sapiens” reveals the reality of
Fermi’s paradox, unless humans can wake up in time.
Since the onset of the
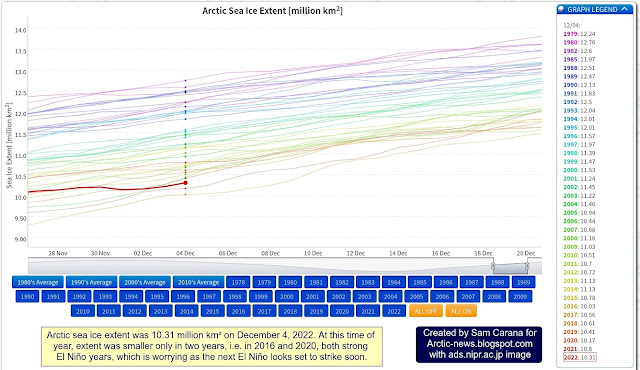
Neolithic about ~10,000 years ago open-ended combustion of wood, coal, oil, methane and gas for production of steam power and electricity (Figure 1), and of uranium to generate nuclear power, constrain the life expectancy of
industrial civilizations through proliferation of greenhouse gases, alteration of the chemistry of the atmosphere and proliferation of nuclear, chemical and biological weapons, testifying to the relevance of Fermi’s paradox in the 20-21 centuries.
Geological and astronomical studies establish Earth is unique among the terrestrial planets in harboring advanced life forms, including colonial life since as early as
~3.5 billion years ago. Should the fate of Homo sapiens be recorded, history would tell that, while the atmosphere was overheating,
oceans acidifying and radioactivity rising, humans never ceased to saturate the atmosphere with greenhouse gases, mine uranium, unleash fatal wars and fire rockets at the planets. All the time indulging in sports games and inundating the airwaves with gratuitous words, false promises, misconstrued assumptions and simple lies ─
betraying their future generations and a multitude of species on the only haven of life known in the solar system.
 |
| Fig. 1. A combined night lights image of Earth signifying global civilization. NASA |
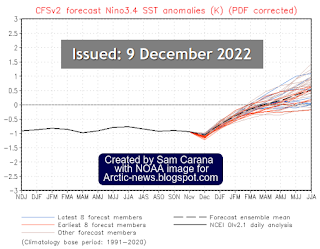
In a new paper titled ‘Global warming in the pipeline’,
Hansen et al. (2022) state: “
glacial-to-interglacial global temperature change implies that fast-feedback equilibrium climate sensitivity is at least ~4°C for doubled CO₂ with likely range 3.5-5.5°C. Greenhouse gas (GHG) climate forcing is 4.1 W/m² larger in 2021 than in 1750, equivalent to 2xCO₂ forcing. Global warming in the pipeline is greater than prior estimates. Eventual global warming due to today's GHG forcing alone -- after slow feedbacks operate -- is about 10°C. Human-made aerosols are a major climate forcing, mainly via their effect on clouds ... A hinge-point in global warming occurred in 1970 as increased GHG warming outpaced aerosol cooling, leading to global warming of 0.18°C per decade.”
The inevitable consequence is a shift in the position of the
Earth’s climate zones, a decline in the
Earth’s albedo (a climatologically significant ~0.5 W/m² decrease over two decades), a rise in greenhouse gases at a geologically unprecedented rate of
2-3 ppm/year), acidification of the oceans (
by about 26 percent),
receding ice sheets, rising sea levels
(~20 cm since 1900), changes in vegetation, forests and soils, a shift in state of the climate and mass extinction, with
humans are driving around one million species to extinction.
For longer than 50 years few were aware that a rise in atmospheric CO₂ on the scale of ~100 ppm CO₂ at the annual rate of 2 - 3 ppm per year, could lead to the unhabitability of large parts of Earth (
The Uninhabitable Earth, by David Wallace-Wells) (Figure 2A). Now we find ourselves surrounded by the consequences ─ hydrocarbon saturation of air and water, runaway global heating, acidification, dissemination of
micro-plastics, habitat destruction,
radioactive overload, proliferation of chemical weapons ─ In confirmation of the reality of
Fermi’s Paradox.
But just at the time the world was increasingly overwhelmed by extreme weather events, severe fires and floods, climate scientists were increasingly ignored, replaced by politicians, bureaucrats, economists, strategists and vested interests ignorant of the basic laws of physics and of the
principles which control the atmosphere-ocean system. Policies and promises guided by the science have been betrayed and meaningful mitigation and adaptation negated by the opening of
new coal mines and gas fields. Cold war strategies violating the United Nation charter were depleting the resources required for mitigation of the looming
climate catastrophe. Within a blink of geological eye, at a rate unprecedented since the extinction of the dinosaurs, large regions of Earth were becoming increasingly uninhabitable for a multitude of species, surpassing 350 ppm CO₂ and approaching Miocene (5.3 – 23.0 Ma)-like conditions (Figure 2B). All along humans continued busily developing a veritable doomsday machine near
1300 nuclear warheads-strong threatening release within seconds.
 |
| Fig. 2. (A) Upper Holocene temperatures. (B). The Middle Miocene long-term continental (brown) and marine (blue) temperature change. Red arrow points to the present (2022) average global temperature of 13.9°C NOAA.
|
That humans are capable of committing the most horrendous crimes upon each other, on other species and on nature, including
mass exterminations, has been demonstrated during the 20th century by the Nazi concentration camps and by
genocidal conflicts such as in Viet Nam, Cambodia, Laos, Rwanda, Yemen, Iraq, Afghanistan, Bosnia, Ukraine ─ the list goes on …
The ultimate step toward the Fermi’s paradox has been reached following nuclear experiments in New Mexico, Novaya Zemlya (Figure 3), the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the rising prospects of a
nuclear war, with consequent firestorms, radiation from fallout, a nuclear winter, and electromagnetic pulses looming ever greater. According to a paper by
Robock and Toon (2012) ‘
Self-assured destruction: The climate impacts of nuclear war’, a thermonuclear war could lead to the end of modern civilization, due to a long-lasting nuclear winter and the destruction of crops. In one model the average temperature of Earth during a
nuclear winter, where black smoke from cities and industries rise into the upper stratosphere, lowers global temperatures by 7 – 8° Celsius for several years.
As stated by
Hansen et al. (2012):
“Burning all fossil fuels would create a different planet than the one that humanity knows. The paleoclimate record and ongoing climate change make it clear that the climate system would be pushed beyond tipping points, setting in motion irreversible changes, including ice sheet disintegration with a continually adjusting shoreline, extermination of a substantial fraction of species on the planet, and increasingly devastating regional climate extremes”.
A nuclear war in the background of carbon saturated atmosphere can only lead to extreme damage to the
life support systems of the planet. The propensity of “sapiens” to genocide and ecocide, are hardly masked by the prevailing Orwellian language of politicians in the absence of meaningful action to avert the demise of the biosphere as we know it. Whereas the ultimate consequences of global heating are likely to occur within a century, including temperature polarities including heat waves and regional cooling of ocean regions by ice melt flow from Antarctica and Greenland ice sheets (
Gikson 2019), a nuclear war on the scale of the MAD (
Mutual Assured Destruction) can erupt on a time scale of minutes …
On July 16, 1945, witnessing the atomic test at the Trinity site, New Mexico, Robert Oppenheimer, the chief nuclear scientist (Figure 4), cited the Hindu scripture of Shiva from the Bhagavad Gita:
“Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds”. Then, as stated by Albert Einstein: “
The splitting of the atom has changed everything, except for man’s way of thinking, and thus we drift into unparalleled catastrophes”.